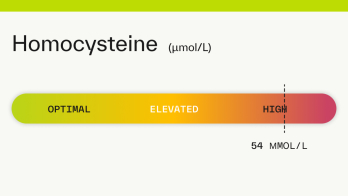
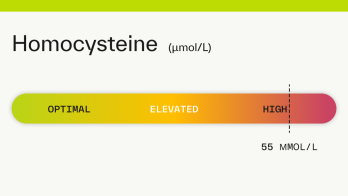
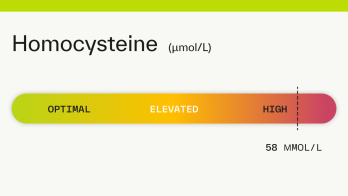
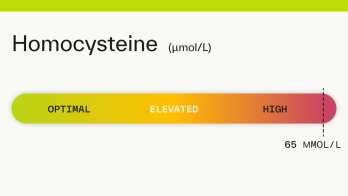
Homocysteine: 53 µmol/L
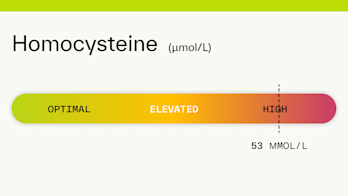
What does a homocysteine level of 53 mean? Are there any symptoms associated with this level?
A homocysteine level of 53 is considered high. High levels of homocysteine (an amino acid in your blood) are often related to a B vitamin deficiency. A homocysteine level >50 µmol/L may damage the lining of your arteries and can increase your risk of blood clots, stroke, heart disease, and heart attack [ 1 5
High homocysteine typically does not cause any symptoms in adults; however, if it’s related to a vitamin B deficiency, you may experience the following symptoms:
Dizziness
Weakness
Changes in mood
Pale skin
Fatigue
Weakness
Tingling hands, arms, legs, or feet
Mouth sores
Swelling of the tongue (folate deficiency)
Anemia
Learn more about homocysteine homocysteine levels
Factors that could contribute to a homocysteine level of 53
Certain factors and health conditions can increase your risk for high homocysteine levels, including [ 1 2
Older age (homocysteine levels can increase as you get older)
Menopause
Being male (men usually have higher homocysteine levels than women)
Drug and tobacco use
Drinking 4 or more cups of coffee a day
Excessive alcohol consumption
Deficiencies in vitamins B12, B6, or folate
Cancer
Psoriasis
Diabetes
Kidney or thyroid problems
Heart disease
Certain variations of the MTHFR gene
Rare inherited diseases, including homocystinuria
What to do if your homocysteine level is 53?
Getting more folic acid (folate), B6, and B12 from foods may help lower your homocysteine level naturally. Some good sources include:
Vitamin B12
: Sardines, clams (including the broth of boiled clams), tuna, trout, beef, milk, and fortified foods like breakfast cereal and nutritional yeastFolate: Fruits, green leafy vegetables, fortified bread and breakfast cereals, lentils, chickpeas, beans, and asparagus
Vitamin B6: Tuna, beef, fortified cereals, milk, chickpeas, chicken, and eggs
Quitting smoking, limiting your alcohol intake
Medications and supplements used to improve homocysteine levels
In addition to making these diet and lifestyle changes, your healthcare provider may recommend certain medications or supplements to help lower your homocysteine level.
Medications
Levothyroxine: For high homocysteine levels caused by hypothyroidism, levothyroxine may be prescribed alongside a folic acid supplement to improve thyroid function and lower homocysteine levels [
3
].Betaine: Also known as betaine anhydrous, or trimethylglycine (TMG), betaine is often prescribed to individuals with homocystinuria along with B vitamin supplements to help control homocysteine levels [
4
].
Supplements
Vitamin B supplements are used to treat high homocysteine caused by a B vitamin deficiency. The common dosage to treat low vitamin B is [ 2
50 mg/day of vitamin B6
1,000 µg (1 mg)/day of vitamin B12
2,400 µg (2.4 mg)/day of folic acid, split into three doses
How Elo can help
If you have high homocysteine or suspect you may have a B vitamin deficiency, Elo Health here
References
Homocysteine: Levels, Tests, High Homocysteine Levels. (2018, December 2). Cleveland Clinic. Retrieved June 8, 2022, from
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/21527-homocysteine
Varga, E. A., Sturm, A. C., Misita, C. P., & Moll, S. (2005). Homocysteine and MTHFR Mutations. Circulation, 111(19).
https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.0000165142.37711.e7
Ziaee, A., Hajibagher Tehrani, N., Hosseinkhani, Z., Kazemifar, A., Javadi, A., & Karimzadeh, T. (2012). Effects of folic acid plus levothyroxine on serum homocysteine level in hypothyroidism. Caspian journal of internal medicine, 3(2), 417–420.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3861905/
Betaine: MedlinePlus Drug Information. (2016, September 15). Retrieved October 3, 2022, from
https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a608012.html
Kuo, H., Sorond, F. A., Chen, J., Hashmi, A., Milberg, W. P., & Lipsitz, L. A. (2005). The Role of Homocysteine in Multisystem Age-Related Problems: A Systematic Review. The Journals of Gerontology, 60(9), 1190–1201.
https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/60.9.1190